Our phones have been integral in the battle against COVID-19 through test and trace frameworks that assisted with containing the infection in places like South Korea and Taiwan. Presently, researchers are saddling cell phones again to recognize Covid particles on surfaces as an extra line of protection against the pandemic, close by more hearty medicines like immunizations and antiviral medications.
Analysts at General Electric have been granted a National Institutes of Health grant to create minuscule sensors that can be installed in mobiles to distinguish the presence of COVID-19 nano-particles.
The group behind the miniature tech asserts that it flaunts similar detection capacities as far larger analytical instruments that you’d normally find in a lab. Following a time of experiments, they guarantee they can tweak the minuscule gadget to confine infection particles without impedance from different elements.
“We have developed tiny sensors smaller than a fingertip that have the same detection capabilities as the high-end analytical instruments the size of a microwave oven. Our sensors are sort of like bloodhounds,” Radislav Potyrailo, a principal scientist at GE Research and principal investigator on the NIH project, explains. “We train them to detect a specific thing, and they are able to do that well without being thrown off the trail by something else.”
Part of the challenge with COVID-19 has been understanding and controlling the spread of infection, especially with regards to asymptomatic cases. Given a few groups can be infectious however give no outward indications of having Covid, overseeing how they conceivably go it on through local area spread has been a main point of contention. That could just turn out to be more squeezing as the inoculated populace develops since while the effect on an immunized individual of COVID-19 might be lower, that doesn’t mean they can’t give the infection to others.
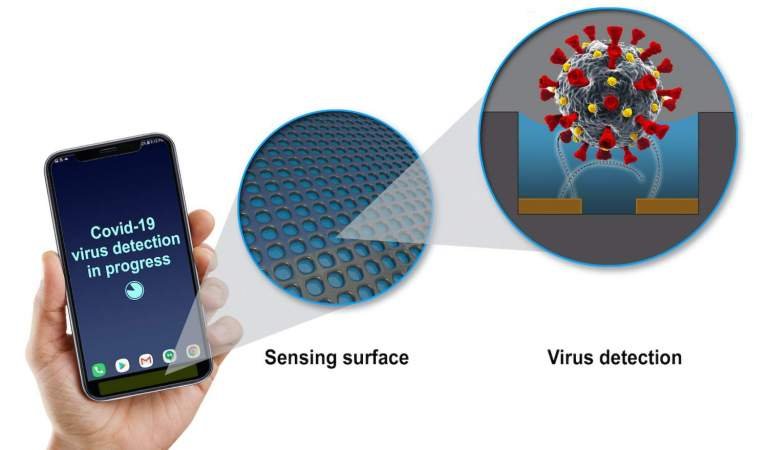
Incorporating detection for the infection into the gadgets and surfaces we connect with consistently could be a vital piece of controlling that spread. While cell phones and other associated gadgets are an undeniable course regardless, one of the allures of biosensor innovation is that low-cost sensors – intended to zero in on distinguishing one or simply a modest bunch of infections – could get undeniably more pervasive.
At the point when you arrive at where sensor exhibits could be fitted to entryway handles and other ordinary surfaces, it gets undeniably more direct to disengage possible vectors for COVID-19 spreading, especially as new variations on the infection arise.
Improvement of the GE sensors is as yet in progress; however, the group says it desires to have built up a practical item before the finish of the long-term NIH project.
