Zinc-Air Battery – New Development
Tesla has bloomed a lot in recent years in the wake of the urge for more green vehicles and for that, there is an increase in demand for power sources. Every day new ways of building a new type of battery are been developed by researchers which could help to store more energy leading to a long time one can drive per charge. This development has lead us to the new technology that is being ventured- Zinc-Air Battery (ZAB). But it comes up with a challenge that it can be sometimes unstable.
Novel Chemistry for Battery
The Zinc-Air Battery can lead to a failure due to the parasitic or side reactions from the use of alkaline electrolytes resulting from dendrite formation and air electrode failure stemming. This difficulty may have been overcome by the researchers by forming novel chemistry for the battery using non-alkaline and water as the electrolyte. The parasitic reaction has been overcome by the new chemistry by the researchers.
The non-alkaline electrolyte for the battery makes use of the former unknown reversible zinc peroxide chemistry. Multiple advantages have been observed by the newly developed non-alkaline electrolyte over the conventional strong alkaline electrolytes. Higher chemical stability and electrochemical reversibility are the advantages of using a zinc anode with more efficiency.
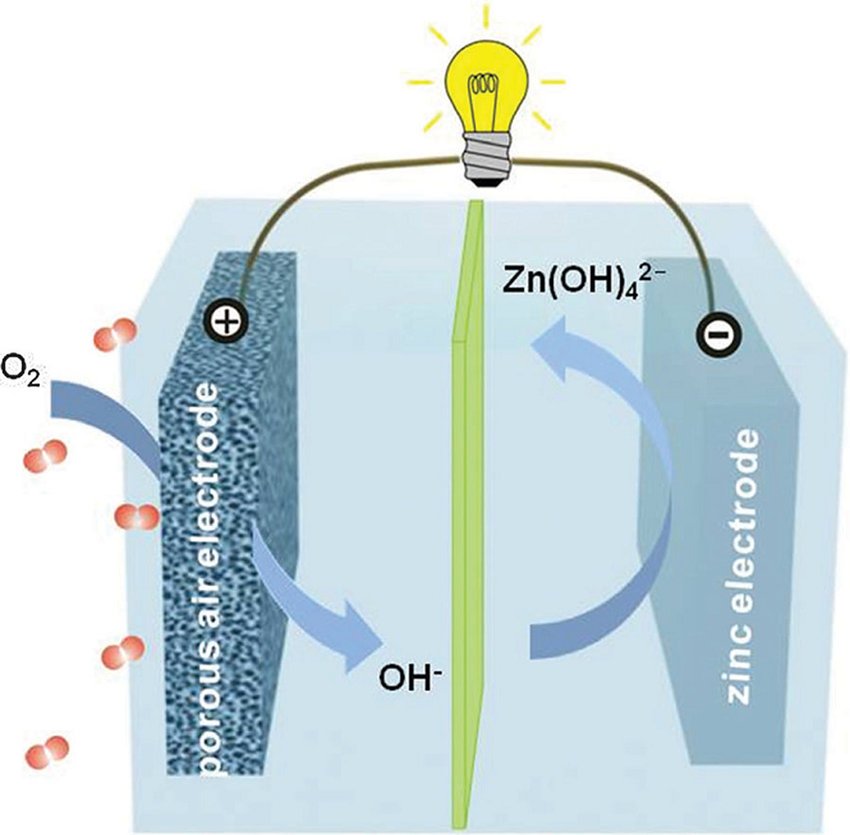
What is happening?
One project researcher said that existing zinc-air batteries use sluggish oxygen redox reactions of four electrons due to the presence of water. However, the team was able to remove water from the air cathode surface using a Zn-salt with the help of a hydrophobic trifluoromethanesulfonate anion, enabling a highly reversible 2e ORR chemical reaction on the air cathode in a diluted, aqueous electrolyte.
Researchers claim that the resulting full zinc-air battery will work stably in an ambient air condition for 320 cycles and 1600 hours. It is clear to researchers that while the ZAB is a potential alternative battery technology with benefits compared to current lithium-ion batteries, more research and optimization is required for the technology. A water management system to ensure the long-term realistic operation is the one remaining problem because the battery operates in an open atmosphere that allows electrolyte evaporation.
